
Back صمام تمدد حراري Arabic Vàlvula d'expansió termostàtica Catalan Expansionsventil German Válvula de expansión termostática Spanish شیر انبساط گرمایی Persian Détendeur thermostatique French Válvula de expansión termostática Galician Valvola di laminazione Italian Smoorventiel Dutch Termostatyczny zawór rozprężny Polish
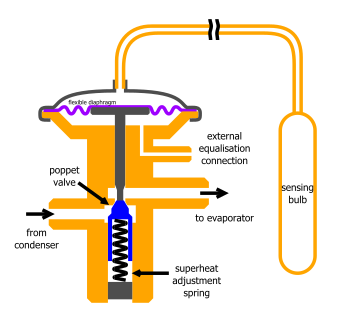
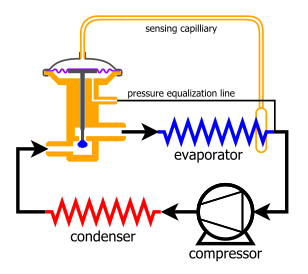
A thermal expansion valve or thermostatic expansion valve (often abbreviated as TEV, TXV, or TX valve) is a component in vapor-compression refrigeration and air conditioning systems that controls the amount of refrigerant released into the evaporator and is intended to regulate the superheat of the refrigerant that flows out of the evaporator to a steady value. Although often described as a "thermostatic" valve, an expansion valve is not able to regulate the evaporator's temperature to a precise value. The evaporator's temperature will vary only with the evaporating pressure, which will have to be regulated through other means (such as by adjusting the compressor's capacity).
Thermal expansion valves are often referred to generically as "metering devices", although this may also refer to any other device that releases liquid refrigerant into the low-pressure section but does not react to temperature, such as a capillary tube or a pressure-controlled valve.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search