
Back حركة مقذوف Arabic প্ৰক্ষেপ্য গতি Assamese Şaquli atılmış cismlər Azerbaijani প্রাসের গতি Bengali/Bangla Kosi hitac BS Tir parabòlic Catalan Vrh šikmý Czech Kasteparabel Danish Wurfparabel German Movimiento parabólico Spanish
This article is currently being merged. After a discussion, consensus to merge this article with Range of a projectile was found. You can help implement the merge by following the instructions at Help:Merging and the resolution on the discussion. Process started in August 2024. |
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

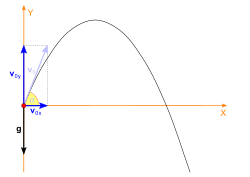

In physics, projectile motion describes the motion of an object that is launched into the air and moves under the influence of gravity alone, with air resistance neglected. In this idealized model, the object follows a parabolic path determined by its initial velocity and the constant acceleration due to gravity. The motion can be decomposed into horizontal and vertical components: the horizontal motion occurs at a constant velocity, while the vertical motion experiences uniform acceleration.
This framework, which lies at the heart of classical mechanics, is fundamental to a wide range of applications—from engineering and ballistics to sports science and natural phenomena.
Galileo Galilei showed that the trajectory of a given projectile is parabolic, but the path may also be straight in the special case when the object is thrown directly upward or downward. The study of such motions is called ballistics, and such a trajectory is described as ballistic. The only force of mathematical significance that is actively exerted on the object is gravity, which acts downward, thus imparting to the object a downward acceleration towards Earth's center of mass. Due to the object's inertia, no external force is needed to maintain the horizontal velocity component of the object's motion.
Taking other forces into account, such as aerodynamic drag or internal propulsion (such as in a rocket), requires additional analysis. A ballistic missile is a missile only guided during the relatively brief initial powered phase of flight, and whose remaining course is governed by the laws of classical mechanics.
Ballistics (from Ancient Greek βάλλειν bállein 'to throw') is the science of dynamics that deals with the flight, behavior and effects of projectiles, especially bullets, unguided bombs, rockets, or the like; the science or art of designing and accelerating projectiles so as to achieve a desired performance.

The elementary equations of ballistics neglect nearly every factor except for initial velocity, the launch angle and a gravitational acceleration assumed constant. Practical solutions of a ballistics problem often require considerations of air resistance, cross winds, target motion, acceleration due to gravity varying with height, and in such problems as launching a rocket from one point on the Earth to another, the horizon's distance vs curvature R of the Earth (its local speed of rotation ). Detailed mathematical solutions of practical problems typically do not have closed-form solutions, and therefore require numerical methods to address.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
