Back بوابة:نجوم Arabic Portail:Étoiles French Portal:Bintang ID Portale:Stelle Italian Portal:Estrelas Portuguese Portal:Stea Romanian Проект:Астрономические объекты/Звёзды Russian Portál:Hviezda Slovak Cổng thông tin:Sao Vietnamese Portal:恒星 Chinese
IntroductionA star is a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by self-gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated 1022 to 1024 stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye—all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material largely comprising hydrogen, helium, and trace heavier elements. Its total mass mainly determines its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due to the thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core. This process releases energy that traverses the star's interior and radiates into outer space. At the end of a star's lifetime as a fusor, its core becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or—if it is sufficiently massive—a black hole. Stellar nucleosynthesis in stars or their remnants creates almost all naturally occurring chemical elements heavier than lithium. Stellar mass loss or supernova explosions return chemically enriched material to the interstellar medium. These elements are then recycled into new stars. Astronomers can determine stellar properties—including mass, age, metallicity (chemical composition), variability, distance, and motion through space—by carrying out observations of a star's apparent brightness, spectrum, and changes in its position in the sky over time. Stars can form orbital systems with other astronomical objects, as in planetary systems and star systems with two or more stars. When two such stars orbit closely, their gravitational interaction can significantly impact their evolution. Stars can form part of a much larger gravitationally bound structure, such as a star cluster or a galaxy. (Full article...) Selected star - Photo credit: NASA/ESA/HST
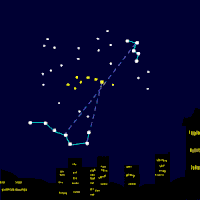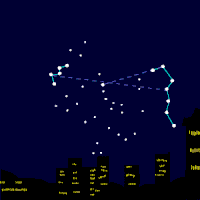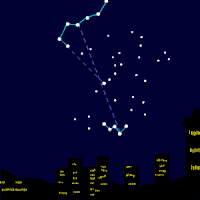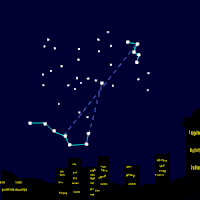
Polaris (α UMi / α Ursae Minoris / Alpha Ursae Minoris, commonly North(ern) Star or Pole Star, or Dhruva Tara and sometimes Lodestar) is the brightest star in the constellation Ursa Minor. It is very close to the north celestial pole (42′ away as of 2006[update], making it the current northern pole star. Polaris is about 430 light-years from Earth and is a multiple star. α UMi A is a six solar massWieland page 3: masses of A and P ... (6.0+1.54M⊙) F7 bright giant (II) or supergiant (Ib). The two smaller companions are: α UMi B, a 1.5 solar mass F3V main sequence star orbiting at a distance of 2400 AU, and α UMi Ab, a very close dwarf with an 18.5 AU radius orbit. There are also two distant components α UMi C and α UMi D. Recent observations show that Polaris may be part of a loose open cluster of type A and F stars. Polaris B can be seen even with a modest telescope and was first noticed by William Herschel in 1780. In 1929, it was discovered by examining the spectrum of Polaris A that it had another very close dwarf companion (variously α UMi P, α UMi a or α UMi Ab), which had been theorized in earlier observations (Moore, J.H and Kholodovsky, E. A.). In January 2006, NASA released images from the Hubble telescope, directly showing all three members of the Polaris ternary system. The nearer dwarf star is in an orbit of only 18.5 AU (2.8 billion km; about the distance from our Sun to Uranus) from Polaris A, explaining why its light is swamped by its close and much brighter companion. Polaris is a classic Population I Cepheid variable (although, it was once thought to be Population II due to its high galactic latitude). Selected article - Photo credit: JAXA/NASA
A solar flare is a large explosion in the Sun's atmosphere that can release as much as 6 × 1025 joules of energy. The term is also used to refer to similar phenomena in other stars, where the term stellar flare applies. Solar flares affect all layers of the solar atmosphere (photosphere, corona, and chromosphere), heating plasma to tens of millions of kelvins and accelerating electrons, protons, and heavier ions to near the speed of light. They produce radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum at all wavelengths, from radio waves to gamma rays. Most flares occur in active regions around sunspots, where intense magnetic fields penetrate the photosphere to link the corona to the solar interior. Flares are powered by the sudden (timescales of minutes to tens of minutes) release of magnetic energy stored in the corona. If a solar flare is exceptionally powerful, it can cause coronal mass ejections. X-rays and UV radiation emitted by solar flares can affect Earth's ionosphere and disrupt long-range radio communications. Direct radio emission at decimetric wavelengths may disturb operation of radars and other devices operating at these frequencies. Solar flares were first observed on the Sun by Richard Christopher Carrington and independently by Richard Hodgson in 1859 as localized visible brightenings of small areas within a sunspot group. Stellar flares have also been observed on a variety of other stars. The frequency of occurrence of solar flares varies, from several per day when the Sun is particularly "active" to less than one each week when the Sun is "quiet". Large flares are less frequent than smaller ones. Solar activity varies with an 11-year cycle (the solar cycle). At the peak of the cycle there are typically more sunspots on the Sun, and hence more solar flares. Selected image - Photo credit: commons:User:Pbroks13
An illustration of the structure of the Sun:
1. Core 2. Radiative zone 3. Convective zone 4. Photosphere 5. Chromosphere 6. Corona 7. Sunspot 8. Granules 9. Prominence Did you know?
SubcategoriesTo display all subcategories click on the ►
Selected biography - Photo credit: State Post Bureau of the People's Republic of China
Zhang Heng (simplified Chinese: 张衡; traditional Chinese: 張衡; pinyin: Zhāng Héng; Wade–Giles: Chang Heng) (CE 78–139) was a Chinese astronomer, mathematician, inventor, geographer, cartographer, artist, poet, statesman and literary scholar from Nanyang, Henan. He lived during the Eastern Han Dynasty (CE 25–220) of China. He was educated in the capital cities of Luoyang and Chang'an, and began his career as a minor civil servant in Nanyang. Eventually, he became Chief Astronomer, Prefect of the Majors for Official Carriages, and then Palace Attendant at the imperial court. His uncompromising stances on certain historical and calendrical issues led to Zhang being considered a controversial figure, which prevented him from becoming an official court historian. His political rivalry with the palace eunuchs during the reign of Emperor Shun (r. 125–144) led to his decision to retire from the central court to serve as an administrator of Hejian, in Hebei. He returned home to Nanyang for a short time, before being recalled to serve in the capital once more in 138. He died there a year later, in 139. Zhang applied his extensive knowledge of mechanics and gears in several of his inventions. He invented the world's first water-powered armillary sphere, to represent astronomical observation; improved the inflow water clock by adding another tank; and invented the world's first seismometer, which discerned the cardinal direction of an earthquake 500 km (310 mi) away. Furthermore, he improved previous Chinese calculations of the formula for pi. In addition to documenting about 2,500 stars in his extensive star catalogue, Zhang also posited theories about the Moon and its relationship to the Sun; specifically, he discussed the Moon's sphericity, its illumination by reflecting sunlight on one side and remaining dark on the other, and the nature of solar and lunar eclipses. His fu (rhapsody) and shi poetry were renowned and commented on by later Chinese writers. Zhang received many posthumous honors for his scholarship and ingenuity, and is considered a polymath by some scholars. Some modern scholars have also compared his work in astronomy to that of Ptolemy (CE 86–161).
TopicsThings to do
Related portalsAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals |
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search