
Back ثنائي فلوريد الأكسجين Arabic اوکسیژن دیفلوئورید AZB Кислороден дифлуорид Bulgarian Difluorid kyslíku Czech Sauerstoffdifluorid German Διφθοριούχο οξυγόνο Greek Difluoruro de oxígeno Spanish اکسیژن دیفلوئورید Persian Happidifluoridi Finnish Difluorure d'oxygène French

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Oxygen difluoride
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.087 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| OF2 | |
| Molar mass | 53.9962 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless gas, pale yellow liquid when condensed |
| Odor | peculiar, foul |
| Density |
|
| Melting point | −223.8 °C (−370.8 °F; 49.3 K) |
| Boiling point | −144.75 °C (−228.55 °F; 128.40 K) |
| hydrolyzes[1] slowly | |
| Vapor pressure | 48.9 atm (at −58.0 °C or −72.4 °F or 215.2 K[a]) |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
43.3 J/mol K |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
246.98 J/mol K |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−24.5 kJ mol−1 |
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
42.5 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[4] | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H270, H280, H314, H330 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LC50 (median concentration)
|
|
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.05 ppm (0.1 mg/m3)[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
C 0.05 ppm (0.1 mg/m3)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
0.5 ppm[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
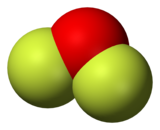
Oxygen difluoride is a chemical compound with the formula OF2. As predicted by VSEPR theory, the molecule adopts a bent molecular geometry. It is a strong oxidizer and has attracted attention in rocketry for this reason.[5] With a boiling point of −144.75 °C, OF2 is the most volatile (isolable) triatomic compound.[6] The compound is one of many known oxygen fluorides.
- ^ "difluorine monoxide; oxygen difluoride, physical properties, suppliers, CAS, MSDS, structure, Molecular Formula, Molecular Weight, Solubility, boiling point, melting point". www.chemyq.com.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0475". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Oxygen difluoride". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ GHS: GESTIS 570242
- ^ "Oxygen Difluoride - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2023-11-03.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 819. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
