
Back Lys van naaste sterre Afrikaans قائمة أقرب النجوم والأقزام البنية Arabic Lis bintang pinih nampek BAN Listn vo de nextn Stean BAR Спіс найбліжэйшых зорак Byelorussian Roll ar stered tostañ Breton Llista d'estrelles més properes Catalan Seznam nejbližších hvězd Czech Liste der nächsten extrasolaren Systeme German Κατάλογος των κοντινότερων αστέρων και φαιών νάνων Greek
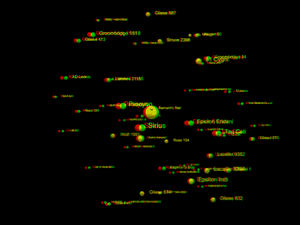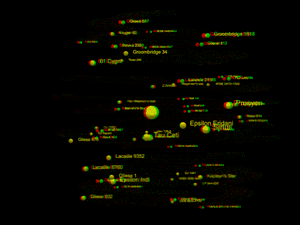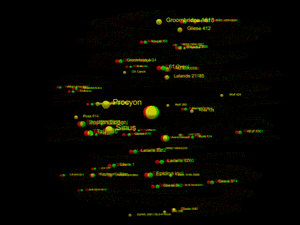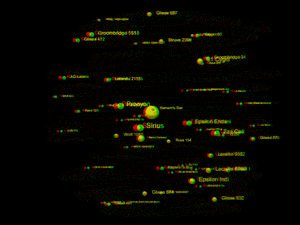
 3D red green glasses are recommended to view this image correctly.
3D red green glasses are recommended to view this image correctly.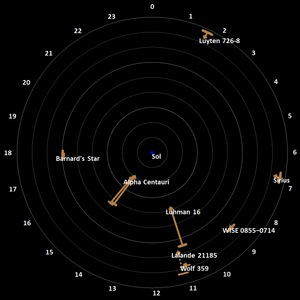
This list covers all known stars, white dwarfs, brown dwarfs, and sub-brown dwarfs within 20 light-years (6.13 parsecs) of the Sun. So far, 131 such objects have been found. Only 22 are bright enough to be visible without a telescope, for which the star's visible light needs to reach or exceed the dimmest brightness visible to the naked eye from Earth, 6.5 apparent magnitude.[1]
The known 131 objects are bound in 94 stellar systems. Of those, 103 are main sequence stars: 80 red dwarfs and 23 "typical" stars having greater mass. Additionally, astronomers have found 6 white dwarfs (stars that have exhausted all fusible hydrogen), 21 brown dwarfs, as well as 1 sub-brown dwarf, WISE 0855−0714 (possibly a rogue planet). The closest system is Alpha Centauri, with Proxima Centauri as the closest star in that system, at 4.2465 light-years from Earth. The brightest, most massive and most luminous object among those 131 is Sirius A, which is also the brightest star in Earth's night sky; its white dwarf companion Sirius B is the hottest object among them. The largest object within the 20 light-years is Procyon.
The Solar System, and the other stars/dwarfs listed here, are currently moving within (or near) the Local Interstellar Cloud, roughly 30 light-years (9.2 pc) across. The Local Interstellar Cloud is, in turn, contained inside the Local Bubble, a cavity in the interstellar medium about 300 light-years (92.0 pc) across. It contains Ursa Major and the Hyades star cluster, among others. The Local Bubble also contains the neighboring G-Cloud, which contains the stars Alpha Centauri and Altair. In the galactic context, the Local Bubble is a small part of the Orion Arm, which contains most stars that we can see without a telescope. The Orion Arm is one of the spiral arms of our Milky Way galaxy.
- ^ Weaver, Harold F. (1947). "The Visibility of Stars Without Optical Aid". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 59 (350): 232–243. Bibcode:1947PASP...59..232W. doi:10.1086/125956.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search