
Back Eerste wet van termodinamika Afrikaans القانون الأول للديناميكا الحرارية Arabic Primer principiu de la termodinámica AST Termodinamikanın birinci qanunu Azerbaijani Першы пачатак тэрмадынамікі Byelorussian Първи закон на термодинамиката Bulgarian তাপগতিবিদ্যার প্রথম সূত্র Bengali/Bangla Prvi zakon termodinamike BS Primer principi de la termodinàmica Catalan یاسای یەکەمی تێرمۆداینامیک CKB
| Thermodynamics |
|---|
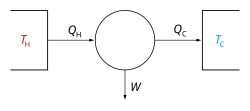 |
The first law of thermodynamics is a formulation of the law of conservation of energy in the context of thermodynamic processes. For a thermodynamic process affecting a thermodynamic system without transfer of matter, the law distinguishes two principal forms of energy transfer, heat and thermodynamic work. The law also defines the internal energy of a system, an extensive property for taking account of the balance of heat transfer, thermodynamic work, and matter transfer, into and out of the system. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form to another. In an externally isolated system, with internal changes, the sum of all forms of energy is constant.
An equivalent statement is that perpetual motion machines of the first kind are impossible; work done by a system on its surroundings requires that the system's internal energy be consumed, so that the amount of internal energy lost by that work must be resupplied as heat by an external energy source or as work by an external machine acting on the system to sustain the work of the system continuously.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search














