Back سيسبلاتين Arabic سیسپلاتین AZB Цисплатин Bulgarian Cisplatin BS Cisplatí Catalan Cisplatin Welsh Cisplatin German Σισπλατίνη Greek Cisplatino Spanish Zisplatino Basque
 | |||
| |||
| Clinical data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Trade names | Platinol, others | ||
| Other names | Cisplatinum, platamin, neoplatin, cismaplat, cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) (CDDP) | ||
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph | ||
| MedlinePlus | a684036 | ||
| License data | |||
| Pregnancy category | |||
| Routes of administration | Intravenous | ||
| ATC code | |||
| Legal status | |||
| Legal status | |||
| Pharmacokinetic data | |||
| Bioavailability | 100% (IV) | ||
| Protein binding | > 95% | ||
| Elimination half-life | 30–100 hours | ||
| Excretion | Renal | ||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
| CAS Number | |||
| PubChem CID | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| UNII | |||
| KEGG | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| PDB ligand | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.036.106 | ||
| Chemical and physical data | |||
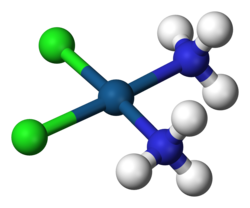
| Formula | [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] | ||
| Molar mass | 300.05 g·mol−1 | ||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| |||
| |||
| | |||
Cisplatin is a chemical compound with formula cis-[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]. It is a coordination complex of platinum that is used as a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of cancers.[2] These include testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, brain tumors and neuroblastoma.[2] It is given by injection into a vein.[2]
Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, hearing problems including severe hearing loss, kidney damage, and vomiting.[2][3][4] Other serious side effects include numbness, trouble walking, allergic reactions, electrolyte problems, and heart disease.[2] Use during pregnancy can cause harm to the developing fetus.[1][2] Cisplatin is in the platinum-based antineoplastic family of medications.[2] It works in part by binding to DNA and inhibiting its replication.[2]
Cisplatin was first reported in 1845 and licensed for medical use in 1978 and 1979.[5][2] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6][7]
- ^ a b c d "Cisplatin Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 12 September 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Cisplatin". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 21 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ Oun R, Moussa YE, Wheate NJ (May 2018). "The side effects of platinum-based chemotherapy drugs: a review for chemists". Dalton Transactions. 47 (19): 6645–6653. doi:10.1039/c8dt00838h. PMID 29632935.
- ^ Callejo A, Sedó-Cabezón L, Juan ID, Llorens J (July 2015). "Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity: Effects, Mechanisms and Protection Strategies". Toxics. 3 (3): 268–293. Bibcode:2015Toxic...3..268C. doi:10.3390/toxics3030268. PMC 5606684. PMID 29051464.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 513. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ World Health Organization (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/345533. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search