
Back Canavanina Catalan Canavanin German Canavanina Spanish Kanavaniini Finnish Canavanine French Canavanina Italian カナバニン Japanese Canavanina Portuguese Kanavanin Serbo-Croatian Kanavanin Serbian
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Canavanine | |
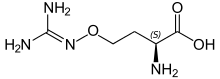
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S)-2-amino-4-{[(diaminomethylidene)amino]oxy}butanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.153.281 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Canavanine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12N4O3 | |
| Molar mass | 176.176 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.61 g·cm−3 (predicted) |
| Melting point | 184 °C (363 °F; 457 K) |
| Boiling point | 366 °C (691 °F; 639 K) |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | insoluble in alcohol, ether, benzene |
| log P | -0.91 (predicted) |
| Vapor pressure | 1.61 μPa (predicted) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.35 (carboxylic acid), 7.01 (oxoguanidinium), 9.22 (ammonium) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H312, H332 | |
| Flash point | 214.6 °C (418.3 °F; 487.8 K) (predicted) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
L-(+)-(S)-Canavanine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid found in certain leguminous plants. It is structurally related to the proteinogenic α-amino acid L-arginine, the sole difference being the replacement of a methylene bridge (-CH
2- unit) in arginine with an oxa group (i.e., an oxygen atom) in canavanine. Canavanine is accumulated primarily in the seeds of the organisms which produce it, where it serves both as a highly deleterious defensive compound against herbivores (due to cells mistaking it for arginine) and a vital source of nitrogen for the growing embryo.[citation needed] The related L-canaline is similar to ornithine.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search